The brilliant cut is the classic cut for diamonds because, when carefully executed and respecting ideal proportions, it maximizes the brilliance and fiery sparkle in the spectral colors of the rainbow.
The brilliant cut diamond is particularly popular for diamond rings, but especially for engagement rings , and forms the classic engagement ring with a prong setting in white gold.
The Anatomy of the Brilliant Cut Diamond
A brilliant-cut diamond consists of a crown, which ends with a table at the top, a girdle, the widest part of the diamond, and a pavilion that tapers downwards.
The arrangement of the various facets follows a fixed pattern. The eight star facets are arranged around the table, which together form the shape of a star. These are followed by the eight diamond-shaped kite facets; the transition to the girdle is provided by the 16 upper girdle facets. The 16 lower girdle facets are connected to the underside, and the lower end is formed by the eight pavilion main facets. Very often you can see that the lower tip of the brilliant-cut diamond is replaced by an additional facet.
The History of the Brilliant Cut
Starting from the natural octahedral shape of a diamond, today's brilliant cut was gradually developed over the centuries.
It was not until the 14th century that the technology to cut diamonds became available; before that, only rough diamonds were known. Initially, the eight surfaces were polished to increase their shine: this type of diamond was called a pointed stone. Subsequently, at the turn of the 14th and 15th centuries, the two points were removed to create a large table on the top and a small culet on the bottom. At the end of the 15th century, the square shape of the diamonds could be varied for the first time - an important step towards the brilliant cut. Additional facets were added, initially an octagonal shape (simple good), followed by increasingly more differentiated and sophisticated variants (double good, triple good).
Diamond rings with brilliant-cut diamonds by RENÉSIM
The brilliant cut and its proportions
By the end of the 17th century, diamonds with 58 facets had already been introduced, but their harmonious arrangement still left much to be desired. In order to bring out the fire inherent in the gemstone – the reflection of the incoming light rays in the colors of the rainbow spectrum – it is necessary to pay attention to certain angles and proportions.
The brilliant cut, as we know it today, was created in 1910 and various research projects were subsequently carried out to determine the ideal dimensions for such a diamond. One result of the attempts to determine the play of colours and the optical effect of a brilliant cut diamond analyze is the Tolkowsky diamond, created in 1919.
This is named after the researcher Marcel Tolkowsky and is still the reference point for a good brilliant cut in the USA today.
In Germany, however, the fine-cut diamond forms the starting point - its proportions were calculated by Eppler in 1949. In Scandinavia, the Scandinavian standard diamond from 1968 is used as a guide.
It is important that the brilliant cut diamond is neither too high nor too flat, otherwise its brilliance will be reduced. In addition, the facets should be arranged symmetrically and evenly.
When buying a diamond, RENÉSIM recommends paying particular attention to whether it has a well-executed cut, as this is crucial for the effect of the gemstone.
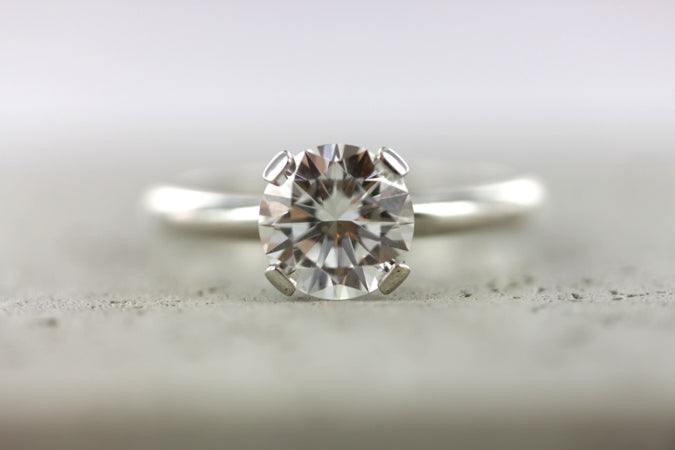

diamond rings from RENÉSIM
Discover unique diamond rings with brilliant cut diamonds from your jeweler RENÉSIM.
At RENÉSIM you will find diamond rings in 18-carat gold alloys (white gold, yellow gold, rose gold) as well as in very fine platinum 950. Choose your favorite model and your favorite diamond from the RENÉSIM First Choice diamond selection and create your unique piece of jewelry.
Diamond rings
diamond jewelry
grindings in the lexicon
Diamond Rating